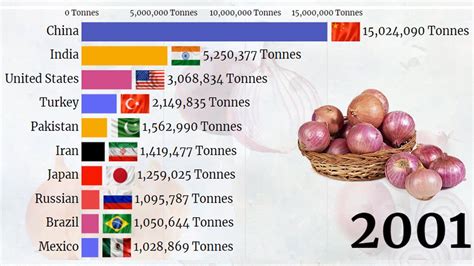
India reigns as the world’s leading onion producer, accounting for a significant portion of global production and consumption, driven by favorable climate, diverse agricultural practices, and robust domestic demand.
India has cemented its position as the world’s foremost onion producer, a title underscored by its substantial contribution to the global supply and its pivotal role in meeting domestic consumption needs. This dominance stems from a confluence of factors, including a conducive climate, varied agricultural methodologies, and consistently high demand within the country. The nation’s onion production not only bolsters its agricultural economy but also impacts global trade dynamics and food security. This report delves into the intricacies of India’s onion production, examining the key drivers, regional contributions, challenges, and the broader implications of its supremacy in the global onion market.
Key Drivers of India’s Onion Production
Several elements converge to facilitate India’s leading position in onion production. These include:
- Favorable Climate: India’s diverse climatic zones allow for onion cultivation throughout the year, ensuring a continuous supply to meet both domestic and international demand. The varying temperature ranges and soil conditions across different regions support the growth of various onion varieties.
- Agricultural Practices: Indian farmers have honed their onion cultivation techniques over generations. These practices include optimal planting schedules, efficient irrigation methods, and the use of both traditional and modern farming technologies. The adoption of high-yield seeds and improved fertilization techniques has further enhanced productivity.
- Domestic Demand: Onions are an integral part of Indian cuisine, used extensively in households, restaurants, and the food processing industry. This consistently high domestic demand provides a stable market for onion farmers, encouraging increased production.
- Government Support: Government policies and initiatives aimed at promoting agricultural development, including subsidies on inputs, irrigation facilities, and market infrastructure, have played a crucial role in boosting onion production. Schemes that provide financial assistance and technical guidance to farmers have also contributed to the sector’s growth.
- Labor Availability: The availability of a large agricultural workforce contributes significantly to onion cultivation. The labor-intensive nature of onion farming, particularly during planting, harvesting, and post-harvest processing, benefits from the readily available workforce in many rural areas.
- Research and Development: Continuous research and development efforts by agricultural universities and research institutions have led to the development of disease-resistant and high-yielding onion varieties. These advancements have helped farmers improve productivity and reduce crop losses.
Regional Contributions to Onion Production
Onion production is not uniformly distributed across India. Certain states have emerged as key contributors, leveraging their specific geographical and climatic advantages.
- Maharashtra: Maharashtra is the largest onion-producing state in India, accounting for a significant share of the country’s total output. The state’s favorable climate, fertile soil, and advanced agricultural practices make it ideal for onion cultivation. Nashik district in Maharashtra is particularly renowned for its high-quality onion production.
- Madhya Pradesh: Madhya Pradesh has emerged as another major onion-producing state, benefiting from its diverse agro-climatic conditions. The state’s onion production has been steadily increasing, contributing substantially to the national supply.
- Karnataka: Karnataka’s onion production is concentrated in certain districts, where farmers have adopted modern farming techniques to enhance productivity. The state’s favorable climate and irrigation facilities support year-round onion cultivation.
- Gujarat: Gujarat’s onion production has been growing, supported by government initiatives and the adoption of improved farming practices. The state’s farmers have been increasingly focusing on high-yielding varieties to meet the growing demand.
- Rajasthan: Rajasthan’s arid and semi-arid regions have also seen significant onion cultivation, with farmers adapting to the challenging climatic conditions through efficient water management techniques.
Challenges in Onion Production
Despite its dominant position, India’s onion production faces several challenges that can impact both the quantity and quality of the crop.
- Climate Variability: Unpredictable weather patterns, including droughts, floods, and extreme temperatures, can significantly affect onion yields. Climate change poses a long-term threat to onion production, requiring farmers to adopt climate-resilient agricultural practices.
- Storage and Post-Harvest Losses: Inadequate storage facilities and poor post-harvest handling practices lead to substantial losses of onions. Lack of cold storage facilities and proper transportation infrastructure contribute to spoilage and reduced market value.
- Pests and Diseases: Onion crops are susceptible to various pests and diseases, which can cause significant yield losses. Effective pest and disease management strategies are essential to protect the crop and ensure high productivity.
- Market Price Fluctuations: Onion prices are highly volatile, influenced by factors such as supply and demand, weather conditions, and government policies. Price fluctuations can negatively impact farmers’ income, making it difficult for them to plan their production and investments.
- Lack of Infrastructure: Inadequate infrastructure, including irrigation facilities, transportation networks, and market infrastructure, hinders onion production and marketing. Improving infrastructure is crucial for reducing post-harvest losses and ensuring efficient supply chain management.
- Limited Access to Credit: Many small and marginal farmers face difficulties in accessing credit for purchasing inputs, investing in irrigation, and adopting modern farming technologies. Providing affordable credit to farmers is essential for enhancing onion production.
- Supply Chain Inefficiencies: Inefficiencies in the supply chain, including multiple intermediaries and inadequate market information, result in higher costs and reduced returns for farmers. Streamlining the supply chain and improving market transparency are crucial for enhancing efficiency.
- Labor Shortages: In some regions, labor shortages during peak seasons can affect onion harvesting and post-harvest processing. Addressing labor shortages through mechanization and improved labor management practices is essential for sustaining onion production.
Impact on Global Trade Dynamics
India’s dominance in onion production has a significant impact on global trade dynamics. The country is a major exporter of onions, supplying to various countries around the world.
- Export Market: India exports onions to a wide range of countries, including Bangladesh, Malaysia, Sri Lanka, Nepal, and the Middle East. The quality and price competitiveness of Indian onions make them attractive to international buyers.
- Price Influence: India’s onion exports can influence global onion prices. When India’s onion production is high, it can lead to lower prices in the international market, benefiting consumers in importing countries. Conversely, when India’s onion production is low, it can lead to higher prices, impacting consumers and importers.
- Trade Policies: India’s trade policies, including export restrictions and tariffs, can significantly affect global onion trade. Export restrictions are sometimes imposed to ensure adequate domestic supply and control prices, which can disrupt the international market.
- Competition: India faces competition from other onion-producing countries, such as China, the United States, and Egypt. These countries also export onions to various markets, competing with India for market share.
- Trade Agreements: Trade agreements with other countries can facilitate onion exports by reducing tariffs and other trade barriers. India has been actively pursuing trade agreements to enhance its onion exports and strengthen its position in the global market.
Strategies for Sustainable Onion Production
To sustain its leading position and address the challenges facing onion production, India needs to adopt strategies that promote sustainable and efficient farming practices.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture: Implementing climate-resilient agricultural practices, such as drought-resistant varieties, water-efficient irrigation methods, and soil conservation techniques, is crucial for mitigating the impact of climate change on onion production.
- Improved Storage Facilities: Investing in modern storage facilities, including cold storage and controlled atmosphere storage, can significantly reduce post-harvest losses and extend the shelf life of onions.
- Integrated Pest and Disease Management: Adopting integrated pest and disease management strategies, including biological control, cultural practices, and judicious use of pesticides, can minimize crop losses and reduce environmental impact.
- Market Information and Price Forecasting: Providing farmers with timely and accurate market information and price forecasts can help them make informed decisions about planting, harvesting, and marketing their produce.
- Supply Chain Management: Streamlining the supply chain by reducing the number of intermediaries, improving transportation infrastructure, and enhancing market transparency can improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Farmer Education and Training: Providing farmers with education and training on modern farming techniques, post-harvest handling practices, and market access can enhance their productivity and profitability.
- Government Support: Continuing government support for onion production, including subsidies on inputs, irrigation facilities, and market infrastructure, is essential for sustaining the sector’s growth.
- Research and Development: Investing in research and development to develop high-yielding, disease-resistant, and climate-resilient onion varieties can help farmers improve productivity and adapt to changing environmental conditions.
- Promoting Value Addition: Encouraging value addition to onions through processing and packaging can enhance their market value and create new opportunities for farmers.
- Water Management: Promoting efficient water management practices, such as drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting, is crucial for conserving water resources and ensuring sustainable onion production.
Technological Advancements in Onion Farming
Incorporating technological advancements can significantly enhance the efficiency and productivity of onion farming.
- Precision Farming: Utilizing precision farming techniques, such as GPS-based soil mapping, variable rate fertilization, and precision irrigation, can optimize input use and improve onion yields.
- Drones: Employing drones for crop monitoring, pest and disease detection, and aerial spraying can help farmers make timely interventions and reduce crop losses.
- Mobile Apps: Developing mobile apps that provide farmers with real-time information on weather conditions, market prices, and best farming practices can enhance their decision-making capabilities.
- Automation: Automating various farming operations, such as planting, harvesting, and sorting, can reduce labor costs and improve efficiency.
- Blockchain Technology: Using blockchain technology to track the movement of onions from farm to market can enhance transparency and improve supply chain management.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Implementing AI-powered systems for predicting crop yields, optimizing irrigation schedules, and detecting pests and diseases can significantly improve onion production.
Economic Impact of Onion Production
Onion production has a significant economic impact on India, contributing to agricultural GDP, employment generation, and export earnings.
- Agricultural GDP: Onion production contributes a substantial share to India’s agricultural GDP. The crop is an important source of income for millions of farmers and agricultural laborers.
- Employment Generation: Onion farming provides employment to a large number of people, particularly in rural areas. The labor-intensive nature of onion cultivation creates numerous job opportunities.
- Export Earnings: Onion exports generate significant foreign exchange earnings for India. The country’s position as the world’s leading onion producer allows it to capitalize on global demand and boost its export revenues.
- Rural Economy: Onion production plays a crucial role in the rural economy, supporting livelihoods and contributing to the overall development of rural areas.
- Food Security: Onion is an essential part of the Indian diet, and its availability at affordable prices is crucial for ensuring food security.
Future Prospects
The future prospects for onion production in India are promising, driven by growing domestic and international demand, technological advancements, and government support.
- Growing Demand: The demand for onions is expected to continue to grow, driven by increasing population, urbanization, and changing dietary habits.
- Technological Advancements: Technological advancements in onion farming are expected to improve productivity, reduce costs, and enhance the quality of the crop.
- Government Support: Continued government support for onion production is expected to sustain the sector’s growth and help farmers overcome the challenges they face.
- Export Opportunities: Expanding export opportunities, particularly in emerging markets, are expected to boost onion exports and generate additional income for farmers.
- Value Addition: Promoting value addition to onions through processing and packaging is expected to create new opportunities for farmers and enhance the competitiveness of Indian onions in the global market.
Conclusion
India’s reign as the world’s top onion producer is a testament to its favorable climate, diverse agricultural practices, and robust domestic demand. While challenges such as climate variability, storage losses, and market price fluctuations persist, strategic interventions, including climate-resilient agriculture, improved storage facilities, and streamlined supply chain management, can ensure the sustainability and growth of the sector. Technological advancements and continued government support will further enhance India’s position in the global onion market, contributing to economic growth, employment generation, and food security. By embracing innovation and sustainable practices, India can continue to feed its own population and supply the world with this essential vegetable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Which country produces the most onions in the world?
India is the largest onion-producing country in the world, accounting for a significant portion of global onion production.
-
Which Indian state is the leading producer of onions?
Maharashtra is the leading onion-producing state in India, contributing a significant share to the country’s total onion output. Nashik district in Maharashtra is particularly famous for its high-quality onion production.
-
What are the main challenges faced by onion farmers in India?
Onion farmers in India face several challenges, including climate variability (droughts, floods, extreme temperatures), inadequate storage facilities leading to post-harvest losses, pest and disease infestations, market price fluctuations, lack of access to credit, and supply chain inefficiencies.
-
How does India’s onion production affect global trade?
As the largest onion producer, India’s production and export policies significantly influence global onion prices and trade dynamics. Export restrictions or high production volumes in India can either increase or decrease global onion prices, impacting importers and consumers worldwide.
-
What strategies can be adopted to improve onion production and reduce post-harvest losses in India?
To improve onion production and reduce post-harvest losses, India can adopt several strategies, including implementing climate-resilient agricultural practices, investing in modern storage facilities (cold storage), adopting integrated pest and disease management, providing farmers with timely market information, streamlining the supply chain, and offering farmer education and training.









